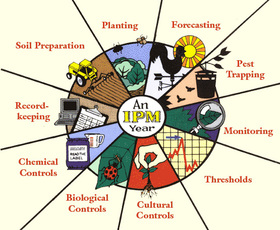
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) means the careful consideration of all available pest control techniques and subsequent integration of appropriate measures that discourage the development of pest populations in an ecologically and economically sound manner.
“Some people think farmers just apply chemicals to their crops to manage pests, but that’s not the case! In fact, the farmers are using a wide variety of tools and techniques to manage pests.”