Pesticide application is necessary to protect crops from pest damages. The main purpose of pesticide application technique is to cover the target with maximum efficiency and minimum efforts to keep the pest under control as well as minimum contamination of non-targets.
Pesticides are formulated in liquid form, powder or granule forms such that it makes possible to apply small quantities of pesticides over large area. The dosage recommendation are generally indicated for acre or hectare e.g. kg/ha or lit/ha or gm ai/ha. Some of the pesticides are applied as low as few gram a.i. per hectare. The desired effect of a pesticide can be obtained only if it is applied by an appropriate method in appropriate time.
The complete knowledge of pest problem i.e., location of the pest (on foliage, under the leaves, at root zone etc), the most susceptible stage of the pest etc. are important to settle proper timing of pesticide application.
The method of pesticide application depends on nature of pests, site of application, type of pesticide formulation, etc. The proper application of pesticides is essential for the control of the crop pest. Besides, the correct and quality pesticide and timely application, the quality of the application has main role in the success of pest control. The rate of application of pesticide should be uniform over the whole of the field area. Too much application as well as too less application of pesticide dose is both undesirable. Therefore adoption of proper Application Technique and ideal equipment is necessary for getting desired outcome of pesticide application.
Most of the pesticides are applied as sprays. Generally EC SC, WP, WDG formulation are diluted suitably with water which is a common carrier of pesticides. Typically following spray volume ranges are taken as guide for field crop spraying.
High Volume Spraying 300 – 500 L/ha
Low Volume Spraying 50 – 150 L/ha
Ultra Low Volume Spraying < 5 L/ha
The spray volume requirement depends on many factors eg. type of crop, growth stage of crop, Sprayer capability, nozzle characteristics, size of spray droplet and number of spray droplets etc. Neither the very small drops nor very big drops are useful due to drift and run off problems. It is obvious that if the spray droplets are coarse-size then the spray volume required will be larger than the small size spray droplets. Also if the thorough coverage (eg. both the sides of leaves) is necessary then the spray volume requirement has to be more.

Knapsack sprayer is widely used spray machine. This type of sprayer is mounded on the back of operator with help of a pair of mounting straps. The pump of the sprayer is actuated by working a hand lever up and down by one hand of the operator and the other hand holds the cut off device for spraying purpose. This sprayer consists of liquid tank, hydraulic pump, operating lever, pressure chamber, agitator, delivery hose, spray lance and nozzle. A bean shaped plastic tank of 14-16 liters capacity is commonly used. The filtered spray solution is filled to 2/3 of the tank capacity. Then the air pump is operated by hand and air pressure (50-60 psi) is built up. The compressed air exerts pressure to move spray liquid to the nozzle via delivery pipe, cut-off device & lance system. It is necessary to operate the hand lever continuously at the rate of 15-20 strokes per minute. The normal working pressure is 40 psi.

The foot operated sprayer is used for orchard and tree spraying. The pump of the sprayer is worked by operating a pedal lever by the foot of the operator. It requires two persons to work. The spray liquid is kept in bucket or container and it is sucked by a suction hose through a filter (strainer) due to piston movement. A suitable ball valve is provided in the piston assembly to serve as suction valve. The liquid from the pump cylinder is then delivered into a pressure chamber where from the pressurized liquid reaches hydraulic nozzle. Hydraulic pressure of 10 kg/cm2 can be achieved which is necessary to project the jet of spray to tall trees. For spraying taller trees, an extra extension like bamboo lance used to gain additional height by 8 – 10 feet.

Commonly used Sprayer nozzles for application of pesticide in field crops Spraying nozzle is a device for emitting spray liquid, breaking it up into small droplets and throwing the droplets away from the nozzle orifice. Different designs of nozzle are used to produce appropriate droplet size spectrum. Generally, Hollow cone nozzle, Fan nozzle and Impact nozzle used for pesticide application in field crops
Hollow cone nozzles: This is a very popular type of hydraulic nozzle for spraying insecticides and fungicide. It produces a hollow cone pattern of spray consisting of mixture of different sizes droplets. The normal working pressure of hollow cone nozzle is about 40 psi. Hollow cone nozzles are good for treating complex targets because spray particles move in infinite angles and various planes providing better penetration of spray. These nozzles are generally not recommended for herbicide application due to possible drift of fine spray particles and difficulty in obtaining an even distribution of spray across the swath. The stainless steel tips or plastic tips are better wear resistant and help consistent spraying.

Fan nozzle: They are also called flat fan nozzles. The spray liquid is thrown from an orifice which is elliptical to give a flat shaped sheet of spray. These are used for band spraying. These nozzles are generally used on booms with proper distance in between and overlapping to give even distribution. The normal working pressure is about 40 psi. However these fan nozzles can also be used for herbicide application but the application is done at low pressure like 15 – 20 psi to avoid drift of fine droplets.

Impact nozzle: These nozzles are also known as deflector nozzles or flood jet nozzles. In these nozzles, the spray liquid emerging from a circular hole strikes an inclined smooth face and is deflected at an angle. The liquid thus spreads as a sheet in a wide angled fan pattern. These nozzles are used for herbicide spraying and are low pressure (15 – 25 psi). The spray pattern essentially consists of coarse droplets.

Adjustable nozzle:
These are also called as triple action nozzle. They are so called because of varying patterns of sprays that can be obtained by manipulating the swirl velocity of spray liquid in the eddy chamber. The hollow cone spray pattern consisting of fine spray particles, or a jet spray for orchard/ tree spraying and a medium coarse spray patterns can be obtained by simple adjustments. These nozzles are generally used with foot operated sprayers, rocking sprayers or high pressure hydraulic sprayers for spraying trees.
The sprayer should be checked and calibrated frequently. Some equipment manufacturers provide tables about use and capacity of their equipment. But it is difficult to always fully relay on such tables. As the sprayer gets old the pump and the nozzle also wear out. The performance of sprayer then changes and rate of application becomes different. The calibration of sprayer, therefore, is essential to make sure that the pesticide is applied correctly and evenly. There are many methods described for calibration of sprayer. The sprayer can be calibrated theoretically and practically in the field. It is good to frequently verify the correctness of theoretical calibration with field practical calibration.
A very simple and easy to remember formula is
F = SDA/10000
Where,
F – Flow rate in L/min
S – Swath width in meter
D – Operator’s walking speed in m/min
A – Application rate in L/ha
The effective swath width depends upon the wind velocity and crop growth, Higher the wind velocity, wider the swath of spray. Pesticide application should not be made when the wind velocity is more than 10 km/hr. This spraying is better done in wind velocity between 3-10 km/hr
Spray Droplets, Sampling and Measurement It is very difficult to define the optimum size of droplet for field application due to diversity of targets.
Different target and optimum droplet size
Flying insects 1 – 50 μm
Insects on foliage 30 – 50 μm
Foliage soil (and avoidance of drift) 250 – 500μm

All nozzles in the field produce ranges of droplets of different size called spray spectrum. The hydraulic nozzles have wide size range of droplets whereas the rotary nozzles have narrow range.
Theoretical number of droplets per cm2 area:
Droplet diameter (μm) No. of drops/cm2
35 512
70 64
140 8
280 1
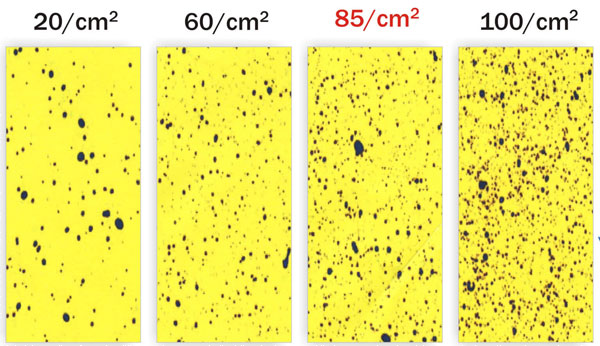
The droplet diameter and the velocity have direct effect on the deposit efficiency. For most field work the qualitative assessment is enough which can indicate the droplet reach, penetration in canopy and droplet deposit density. But for accurate study of pesticide quantity deposit (μgm/cm2) the quantitative assessment is needed.
Operator should wear protective clothing such as Sun shed cap, face mask/face shield, safety glasses, hand gloves and full length trousers and shirts during handling and application of pesticide.
The mixing of pesticide should be done very carefully. It involves handling of concentrated formulations. It is good to wear hand gloves while opening pesticide container, pouring/measuring the formulation and stirring the solution. If the concentrated formulation spills on hand or other body parts, it should be washed off thoroughly with water immediately.

The measurement of small quantity of formulation should be done with the help of measuring cylinder. The mixture should be stirred with a long stick and never by hand. For preparing spray mix with wettable powder, first prepare a paste of required quantity of wettable powder with small quantity of water and subsequently add this paste to the desired quantity of water and stir well. To help uninterrupted spraying always use clean water and use filter when filling solution into spray tank. The spray solution should not be prepared more than what can be sprayed during the day. The pesticide effect of dilute solutions becomes less if solution is left overnight.

The operator should always walk across the prevailing wind direction so that the spray is always moving away from his body. The operator need not pump continuously so that he can divert his attention to better coverage. The spray nozzle should be held and aimed at rows which are about one meter away from the nozzle and the operator should try to create a little fluttering of leaves to improve coverage.
General care & maintenance of sprayer
Proper pesticide application cannot be done without good quality Plant Protection Equipment. A well designed machine shall be efficient as far as pesticide distribution and delivery to the target in minimum time with minimum wastages is concerned. Following general care & maintenance of sprayer is needed for optimum performance of plant protection equipment:
- Clean the equipment before and after work is over.
- Nozzle parts should be cleaned with a brush.
- Clean outer surface with brush or waste fabric by using plenty of water.
- Flush the equipment with clean water to wash inside parts of containers, tubes and nozzles to be free from chemicals.
- Oil the moving parts with lubricating oil or grease, if needed.
- Do not drop the equipment or attachments on the ground.
- Lances and nozzles should not keep on the ground.
- Equipment should be stored in clean & dry space, duly protected from sun and rain
Other methods of pesticide application
Application of Granular formulation:
Broadcasting: Granular formulation of pesticide is mixed with equal quantity of sand and broadcasted directly on the soil or in thin film of standing water and impounds water for 3 days.
In-furrow application: Granular formulation of pesticide is applied at the time of sowing in furrows in beds and covered with soil before irrigation.
Side dressing: After the establishment of the plants, the Granular formulation of pesticide is applied a little away from the plant (10-15 cm) in a furrow.
Spot application: Granular formulation of pesticide is applied @ 5 cm away and 5 cm deep on the sides of plant.
Ring application: Granular formulation of pesticide applied in a ring form around the trees.
Root zone application: Granular formulation of pesticide encapsulated and placed in the root zone of the plant
Leaf whorl application: Granular formulation of pesticide is applied by mixing it with equal quantity of sand in the central whorl of crops to control internal borers.
Pralinage : The surface of sucker intended for planting is trimmed. The sucker is dipped in wet clay slurry and Granular formulation of pesticide is sprinkled to control burrowing nematode.
Application of pesticides for seed/seedling/sett treatment
Seed pelleting/seed dressing: Before sowing of seed, it is mixed with Insecticide and/or fungicide then shade dried.
Seedling root dip: A shallow pit lined with polythene sheet is prepared in the field and pored necessary amount of urea, spray mix of pesticide and water. The roots of seedlings in bundles are dipped for a certain time in the pit before transplanting.
Sett treatment: Setts are dipped in spray mix of pesticide for certain time.

Application of pesticides in large trees
Trunk/stem injection: Drill a downward slanting hole of 1.25 cm diameter to a depth of 5 cm at a light of about 1.5 m above ground level. In this method, required amount of pesticide inject into the stem and plug the hole with cement (or) clay mixed with a fungicide. Pesticide also used with an injecting gun or hypodermic syringe in Pseudo stem for pest control
Padding: Bark of infested tree (5 x 5 cm) is removed on three sides leaving bottom as a flap. Cotton is placed in the exposed area and add required amount of insecticide solution in it then cover with fungicide mix clay material.
Swabbing: In this method the trunk and branches of tree swab with necessary pesticide.
Soil drenching: Pesticide formulation mix with water and the mix is used to drench the soil to control certain pests.
Capsule placement: The systemic pesticide is applied in capsules to get toxic effect for a long period.
Baiting
Bait for insect: Small pellets of bait prepared with required amount of molasses, pesticides, rice bran and water and dropped in the field in the evening hours.
Bait for rats: Rodenticide is mixed at 1:49 ratio with food like popped rice or maize. Ready to use cake formulation is also available.
Fumigation
Soil: To control the nematode in soil, the liquid fumigants are injected by using injecting gun.
Storage: Liquid fumigants or solid fumigant are recommended in godowns to control stored product pest.
Trunk: Solid fumigant is inserted into the affected portion and plugged with cement or mud for the control of insect

